
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy “PCC in Construction” Matters More Than You Think
When you think about building a home in Delhi or NCR, the big questions are usually about cost, layout, and timelines. Yet one quiet detail — PCC in construction — often decides whether your structure stands solid for decades or cracks within years.
From Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) under your footings to Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC) beams that hold your walls upright, understanding where each belongs can save you money, rework, and headaches.
In this blog, we decode the PCC vs RCC debate for Delhi homeowners — what each does, where it makes sense, what IS codes say, typical Delhi-NCR costs, and how leading builders like Hindpride Construction ensure both strength and sustainability in every pour.
Plain Cement Concrete (PCC) is the unsung hero of every project. It’s the base layer beneath your RCC footings or slabs, providing a clean, level surface that isolates structural concrete from soil and moisture.
Delhi homeowners often overlook PCC in construction as a “non-structural” step, but skipping it leads to uneven footing levels, moisture ingress, and long-term settlement cracks.
Where PCC ends, RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) begins. This is the mix that takes both compression and tension loads, thanks to embedded steel reinforcement.
Where You’ll See RCC:
Typical RCC Grades:
IS 456:2000 and IS 10262:2019 govern RCC design, mix proportioning, and durability checks.
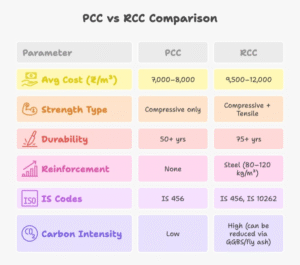
Parameter | PCC (Plain Cement Concrete) | RCC (Reinforced Cement Concrete) |
Reinforcement | None | Contains steel bars |
Load-bearing capacity | Only compressive | Compressive + tensile |
Typical mix | 1:4:8, 1:3:6 | M20+ |
Use | Leveling base, blinding, sub-floor | Structural elements |
IS Code | IS 456:2000 | IS 456:2000, IS 10262:2019 |
Cost range (Delhi, 2025) | ₹7,000–₹8,000 per m³ | ₹9,500–₹12,000 per m³ |
(Use these cost ranges illustratively, cross-link to the cost page for live rates.)
Delhi-NCR sits on alluvial soil with high moisture variability, especially in areas near the Yamuna belt, Dwarka Expressway, and Noida Extension. This makes PCC in construction essential to:
In areas like Gurgaon and Dwarka, fluctuating water tables make the PCC bed an insurance policy against future cracking or dampness.
“You can’t see PCC once the foundation is done — but you’ll feel its absence years later.”
Use PCC when:
Use RCC when:
A rule of thumb from structural engineers:
“If it supports load, it’s RCC. If it supports RCC, it’s PCC.”
Case 1: Gurgaon Independent Floor
Case 2: South Delhi Basement Construction
Case 3: Noida Plot Home
A compliant builder ensures:
✅ Proper mix ratio (1:4:8 or 1:3:6 for PCC).
✅ Thickness as per drawing (min. 75–100 mm).
✅ Cubes tested for every RCC batch.
✅ Reinforcement checked before pouring.
Item | PCC | RCC |
Average rate (₹/m³) | ₹7,000–₹8,000 | ₹9,500–₹12,000 |
Materials | Cement, sand, aggregate | Cement, sand, aggregate, steel |
Labour intensity | Low | High |
Testing | Simple visual check | Cube tests, slump, cover meter |
Maintenance | Minimal | Structural inspection advised every 3–5 years |
👉 These costs are indicative — real values depend on site access, design grade, curing method, and reinforcement weight.
For live updates, refer to:
PCC must project 75 mm beyond the footing on all sides and be cured for at least 2 days before RCC placement.
✅ Check soil firmness before pouring PCC
✅ Confirm mix proportion with site engineer
✅ Ensure cover blocks are in place for RCC
✅ Verify cube test reports for every batch
✅ Never pour PCC and RCC without proper curing interval
Hindpride follows zero-compromise QA — from cube testing to 3-level site inspection.
FAQs
Whether you’re building a 2BHK in Noida or a villa in Gurgaon, knowing where PCC in construction fits in and where RCC takes over can help you:
At Hindpride Construction, we believe every layer — even the one you’ll never see — deserves the same precision. Because great homes start below the surface.
Get your free foundation audit & BoQ with transparent PCC/RCC breakup — Contact Hindpride Today.


